Getting Started with the MKR MEM Shield
The MKR MEM shield allows a MKR board to read and write an SD card using the SD library and also contains 2MB of serial flash memory available for your program data or OTA updates. Flash and SD are managed on the same SPI bus and should be selected through the proper CS pin.
Usage notes
Refer to the SD library for usage examples of the SD memory card. Refer to the Paul Stoffregen's SerialFlash lib to find how to use the onboard 2MB serial flash memory. Please note that on the MKR MEM Board, the Serial Flash uses CS pin 5 instead of 6. All the library examples from Paul's lib need this CS pin changed from 6 to 5.
You can download it using the Library Manager available in the Sketch -> Include library dropdown, in the first position.
As a bonus, this board has a prototype area where you can build additional circuitry. Please note that this shield uses some pins and others are reserved for other shields compatibility; these pins are D4, D6, D8-D12
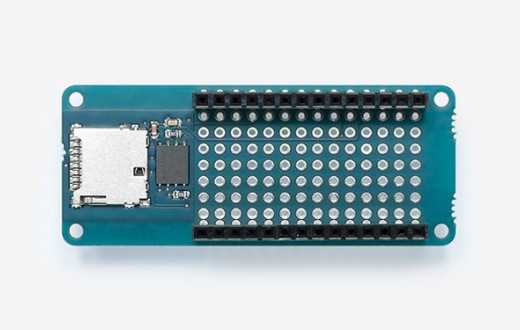
PIN usage
This shield is compatible with the MKR family of Arduino boards.
| Pin number | Usage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | SD CS | No INT |
| 5 | FLASH CS | |
| 8 | MOSI | Reserved |
| 9 | SCK | Reserved |
| 10 | MISO | Reserved |
Example
This is an example from Paul Stoffregen's SerialFlash library that copies data from microSD card to Flash memory. Here you learn how to use both types of memories at the same time.
#include <SerialFlash.h>
#include <SD.h>
#include <SPI.h>
const int SDchipSelect = 4; // Audio Shield has SD card CS on pin 10
const int FlashChipSelect = 5; // digital pin for flash chip CS pin
//const int FlashChipSelect = 21; // Arduino 101 built-in SPI Flash
void setup() {
//uncomment these if using Teensy audio shield
//SPI.setSCK(14); // Audio shield has SCK on pin 14
//SPI.setMOSI(7); // Audio shield has MOSI on pin 7
//uncomment these if you have other SPI chips connected
//to keep them disabled while using only SerialFlash
//pinMode(4, INPUT_PULLUP);
//pinMode(10, INPUT_PULLUP);
Serial.begin(9600);
// wait up to 10 seconds for Arduino Serial Monitor
unsigned long startMillis = millis();
while (!Serial && (millis() - startMillis < 10000)) ;
delay(100);
Serial.println("Copy all files from SD Card to SPI Flash");
if (!SD.begin(SDchipSelect)) {
error("Unable to access SD card");
}
if (!SerialFlash.begin(FlashChipSelect)) {
error("Unable to access SPI Flash chip");
}
File rootdir = SD.open("/");
while (1) {
// open a file from the SD card
Serial.println();
File f = rootdir.openNextFile();
if (!f) break;
const char *filename = f.name();
Serial.print(filename);
Serial.print(" ");
unsigned long length = f.size();
Serial.println(length);
// check if this file is already on the Flash chip
if (SerialFlash.exists(filename)) {
Serial.println(" already exists on the Flash chip");
SerialFlashFile ff = SerialFlash.open(filename);
if (ff && ff.size() == f.size()) {
Serial.println(" size is the same, comparing data...");
if (compareFiles(f, ff) == true) {
Serial.println(" files are identical :)");
f.close();
ff.close();
continue; // advance to next file
} else {
Serial.println(" files are different");
}
} else {
Serial.print(" size is different, ");
Serial.print(ff.size());
Serial.println(" bytes");
}
// delete the copy on the Flash chip, if different
Serial.println(" delete file from Flash chip");
SerialFlash.remove(filename);
}
// create the file on the Flash chip and copy data
if (SerialFlash.create(filename, length)) {
SerialFlashFile ff = SerialFlash.open(filename);
if (ff) {
Serial.print(" copying");
// copy data loop
unsigned long count = 0;
unsigned char dotcount = 9;
while (count < length) {
char buf[256];
unsigned int n;
n = f.read(buf, 256);
ff.write(buf, n);
count = count + n;
Serial.print(".");
if (++dotcount > 100) {
Serial.println();
dotcount = 0;
}
}
ff.close();
if (dotcount > 0) Serial.println();
} else {
Serial.println(" error opening freshly created file!");
}
} else {
Serial.println(" unable to create file");
}
f.close();
}
rootdir.close();
delay(10);
Serial.println("Finished All Files");
}
bool compareFiles(File &file, SerialFlashFile &ffile) {
file.seek(0);
ffile.seek(0);
unsigned long count = file.size();
while (count > 0) {
char buf1[128], buf2[128];
unsigned long n = count;
if (n > 128) n = 128;
file.read(buf1, n);
ffile.read(buf2, n);
if (memcmp(buf1, buf2, n) != 0) return false; // differ
count = count - n;
}
return true; // all data identical
}
void loop() {
}
void error(const char *message) {
while (1) {
Serial.println(message);
delay(2500);
}
}The text of the Arduino getting started guide is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Code samples in the guide are released into the public domain.