Memsic 2125 Accelerometer
The Memsic 2125 (datasheet) is a two-axis accelerometer capable of measuring acceleration up to plus or minus 2g. It has a simple digital interface: two pins (one for each axis) emit pulses whose duration corresponds to the acceleration of that axis. By measuring the length of that pulse, in microseconds, using the pulseIn() function, it is possible to determine the rate of acceleration and to use that data for your purposes.
Hardware Required
Arduino Board
Memsic 2125 Accelerometer
hook-up wires
breadboard
Circuit
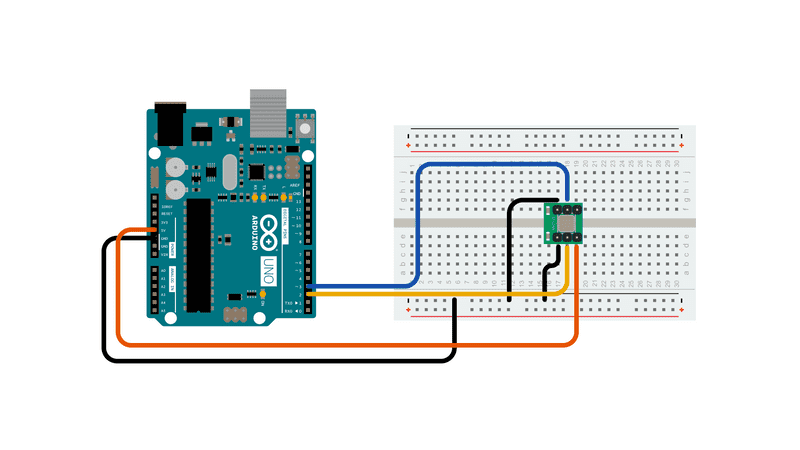
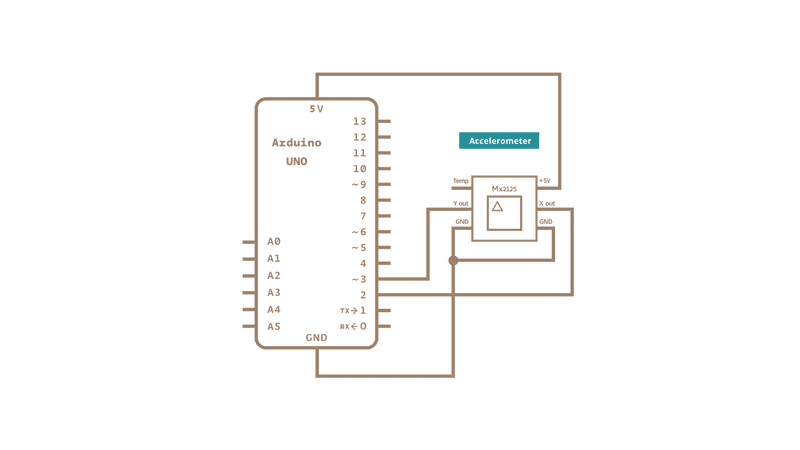
Use the small triangle on the Memsic to properly orient the sensor on your breadboard. Connect the 5V and GND pins of the Memsic 2125 to the power and ground ports on the board. Connect digital pin 2 of the board to the X out pin of the accelerometer, and digital pin 3 to the Y out pin.
Your Arduino must be connected to your computer in order for it to transmit serial data.
Schematic
Code
Open the Serial Monitor of the Arduino Software (IDE) to see the values read from the accelerometer position.
/*
Memsic2125
Read the Memsic 2125 two-axis accelerometer. Converts the pulses output by the
2125 into milli-g's (1/1000 of Earth's gravity) and prints them over the
serial connection to the computer.
The circuit:
- X output of accelerometer to digital pin 2
- Y output of accelerometer to digital pin 3
- +V of accelerometer to +5V
- GND of accelerometer to ground
created 6 Nov 2008
by David A. Mellis
modified 30 Aug 2011
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Memsic2125
*/
// these constants won't change:
const int xPin = 2; // X output of the accelerometer
const int yPin = 3; // Y output of the accelerometer
void setup() {
// initialize serial communications:
Serial.begin(9600);
// initialize the pins connected to the accelerometer as inputs:
pinMode(xPin, INPUT);
pinMode(yPin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// variables to read the pulse widths:
int pulseX, pulseY;
// variables to contain the resulting accelerations
int accelerationX, accelerationY;
// read pulse from x- and y-axes:
pulseX = pulseIn(xPin, HIGH);
pulseY = pulseIn(yPin, HIGH);
// convert the pulse width into acceleration
// accelerationX and accelerationY are in milli-g's:
// Earth's gravity is 1000 milli-g's, or 1 g.
accelerationX = ((pulseX / 10) - 500) * 8;
accelerationY = ((pulseY / 10) - 500) * 8;
// print the acceleration
Serial.print(accelerationX);
// print a tab character:
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(accelerationY);
Serial.println();
delay(100);
}See Also
pinMode()
pulseIn()
ADXL3xx - Read an ADXL3xx accelerometer.
Knock - Detect knocks with a piezo element.
Ping - Detect objects with an ultrasonic range finder.
Last revision 2015/07/29 by SM