
As a STEAM-based learning company, we know how important it is to teach STEAM subjects - and we are wholeheartedly committed to putting technology into the hands of as many students and educators as we can. But we don’t believe it’s the be-all and end-all.
Teaching future skills is so critical to enabling students to thrive and succeed that giving them the tools like problem-solving, critical thinking, and collaboration might be even more important than what they actually learn.
What are STEAM skills?
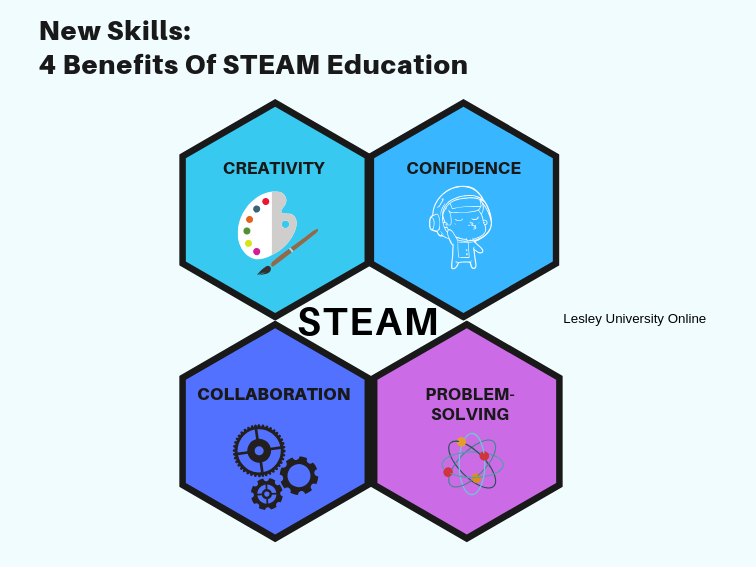
Aside from the technical skills, also known as hard skills in scientific pursuit, the STEAM curriculum also seeks to enhance the soft skills that are crucial in the real world. The integration of the arts in a technical curriculum makes it possible for students to be more adaptive by enhancing the following core soft skills:
* Creativity
Creativity emphasizes the importance of not being restricted by established rules or methodologies. Students will learn how to be more expressive and innovative in their approach.
* Problem-solving
This is not only about solving mathematical equations or trying to balance chemical equations. It’s also about approaching complex and multifaceted problems from different angles through an integrated multidisciplinary approach.
* Collaboration
Students’ emotional intelligence and social skills are enhanced by projects that require collaboration and cooperation among groups. It’s about applying the collective brain power of the students to accomplish a project.
* Confidence
This has more to do with developing intrapersonal intelligence of knowing one’s self much better in terms of abilities, limitations, and purpose. It’s about developing the confidence to apply knowledge while working in a collaborative, interdisciplinary environment.
 (source: https://www.teachthought.com/technology/benefits-of-steam-education/)
(source: https://www.teachthought.com/technology/benefits-of-steam-education/)
Why is STEAM education important for the future?
The nature of the job market and the workplace is changing, and becoming less regimented and more flexible. It’s now more collaborative than individualistic and focuses more on creativity than technical aspects. That’s why a rounded STEAM education is important. Case in point: the computer game industry.
It’s not sufficient anymore to know how to write lines of code; it is also equally important or rather more crucial to be creative in developing new apps. It is important to be multiskilled and be a perpetual learner in a world that is becoming more automated. Some future jobs may be something totally alien or unimaginable to us right now.
Making the minds of tomorrow
In the modern world we live in, change occurs all around us at a seemingly exponential rate. Some of the skills that were deemed essential a decade ago are now obsolete, with this trend inevitably set to continue as the world is re-shaped and revolutionized. In fact, the World Economic Forum has stated that a ‘global reskilling revolution’ is necessary, with 42% of core skills set to change.
This huge shift comes as a result of the technological revolution, with 133 million new jobs expected to be created in the next decade. It’s therefore vital that the generations of the future are suitably skilled in order to live, work, and thrive in a whole new environment. While many of these skills will undoubtedly be rooted in technological or scientific fields, there is also a growing need for people to develop interaction-centric skills such as creativity, collaboration, and interpersonal dynamics.
Therefore, it’s apparent that STEAM learning is essential for equipping young people for a successful future, but there's also an all-important, underlying skill-set designed with the future in mind.
Knowledge for a new age
When considering the types of skills that will remain relevant in the future, you can simply start by eliminating any that will probably be automated. For example, nursing and caregiving is something that will always require a human touch coupled with empathy, making any relevant skills essential in education.
Despite there being some roles that are unlikely to change, many of the jobs that your current students will end up doing may not even exist yet. A 2016 report published by Microsoft and The Future Laboratory stated that 65% of today’s students will be doing jobs that we currently don’t have a real concept of.
There has been an abundance of research conducted around this area, with leading futurists and scientists around the world offering up their thoughts as to what factors are going to drive workplace changes, and what new roles are likely to emerge as a result.
One common theme throughout many examples of research is that educators must instill in their students a love of learning, because they will need to be able to adapt in an ever-changing environment and continue to learn to work with new technologies.
A shifting skillset - driving factors and the predicted results
So, what does all of this equate to when it comes down to the actual skills that students are likely to need? In 2011, the Institute for the Future identified six specific drivers that were shaping the landscape and what skills this would be likely to lead to. The results were as follows:
- Transdisciplinarity
- Sense-making
- New media literacy
- Novel and adaptive thinking
- Social intelligence
- Computational thinking
- Cognitive load management
- Cross-cultural competency
- Design mindset
- Virtual collaboration
While this may differ from existing examples of the skills currently being taught in education, it serves as an interesting comparison against which we might measure exactly how essential skills have been altered and affected by the changing world. It’s also easy to identify that while STEAM remains a vital component for future-proofing the minds of tomorrow, there are also certain necessary skills that are rarely encountered in that realm, such as social intelligence, communication, problem-solving, and cross-cultural competency.
As we move into a more connected age, it’s apparent that people won’t be staying in the same roles for as long as before, with the Millennial generation already described as ‘job hoppers’, making transdisciplinarity arguably the most important skill that educators can equip students with.
While STEAM learning undoubtedly equips students for the advances in AI, coding, and technological progress, giving them a love of learning and providing them with the skills they need to tackle challenges and solve problems will prepare them for whatever future they choose.
Are you an educator looking for STEAM resources for middle school, high school or university? Take a look at Arduino Education kits and how they can support your hands-on STEAM lessons.